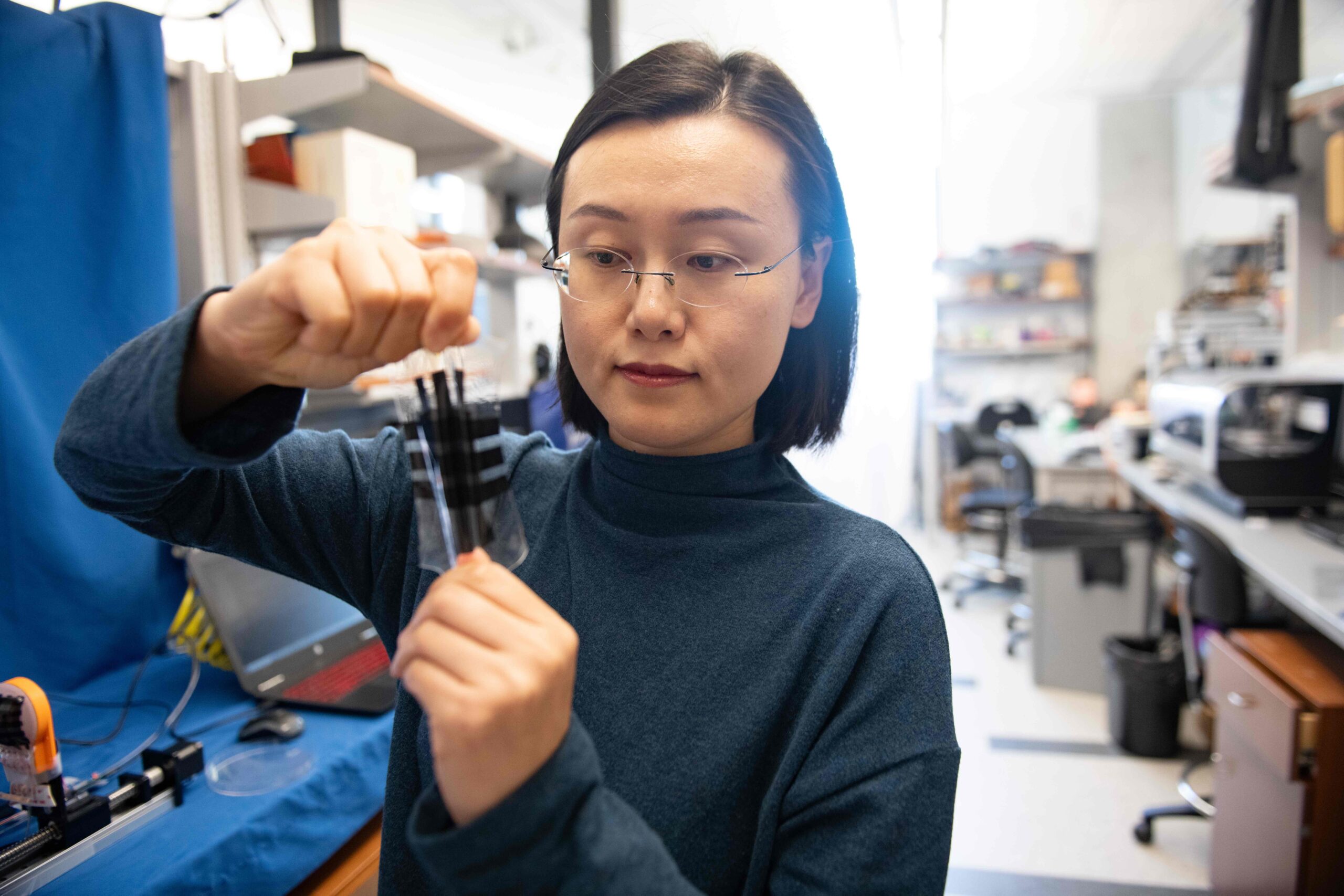
Stretchable E-Skin Could Give Robots Human-Level Touch Sensitivity
AUSTIN, Texas — A first-ever stretchy electronic skin could equip robots and other devices with the same softness and touch sensitivity as human skin,news.utexas.edu
Navigation
Install the app
How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: this_feature_currently_requires_accessing_site_using_safari
More options
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Science! (3 Viewers)
- Thread starterbonnjer
- Start date
- Latest activity Latest activity:
- Joined
- Jul 18, 1998
- Messages
- 22,399
- Reaction score
- 46,365
Offline
Bumblebee nests may be overheating, killing off broods and placing one of the Earth’s critical pollinators in decline as temperatures rise, new research has found.
Around the world, many species of Bombus, or bumblebee, have suffered population declines due to global heating, the research said. Bumblebee colonies are known for their ability to thermoregulate: in hot conditions, worker bees gather to beat their wings and fan the hive, cooling it down. But as the climate crisis pushes average temperatures up and generates heatwaves, bumblebees will struggle to keep their homes habitable.
Most bumblebee broods would not survive at temperatures above 36C, the paper, published in Frontiers in Bee Science, concluded. The research team reviewed 180 years of literature, and found that for all bumblebee species studied the optimum temperature range for incubating nests was between 28C and 32C.
Peter Kevan, the lead author of the study, told the Guardian: “If [bumblebees] can’t keep temperatures below what is probably a lethal limit of about 35C, when the brood may die, that could explain why we are losing so many bumblebees around the world, especially in North America and Europe.”……

 www.theguardian.com
www.theguardian.com
Around the world, many species of Bombus, or bumblebee, have suffered population declines due to global heating, the research said. Bumblebee colonies are known for their ability to thermoregulate: in hot conditions, worker bees gather to beat their wings and fan the hive, cooling it down. But as the climate crisis pushes average temperatures up and generates heatwaves, bumblebees will struggle to keep their homes habitable.
Most bumblebee broods would not survive at temperatures above 36C, the paper, published in Frontiers in Bee Science, concluded. The research team reviewed 180 years of literature, and found that for all bumblebee species studied the optimum temperature range for incubating nests was between 28C and 32C.
Peter Kevan, the lead author of the study, told the Guardian: “If [bumblebees] can’t keep temperatures below what is probably a lethal limit of about 35C, when the brood may die, that could explain why we are losing so many bumblebees around the world, especially in North America and Europe.”……

Bumblebee nests are overheating to fatal levels, study finds
More frequent heatwaves mean bees are unable to thermoregulate their hives – further endangering a species already in decline
Offline
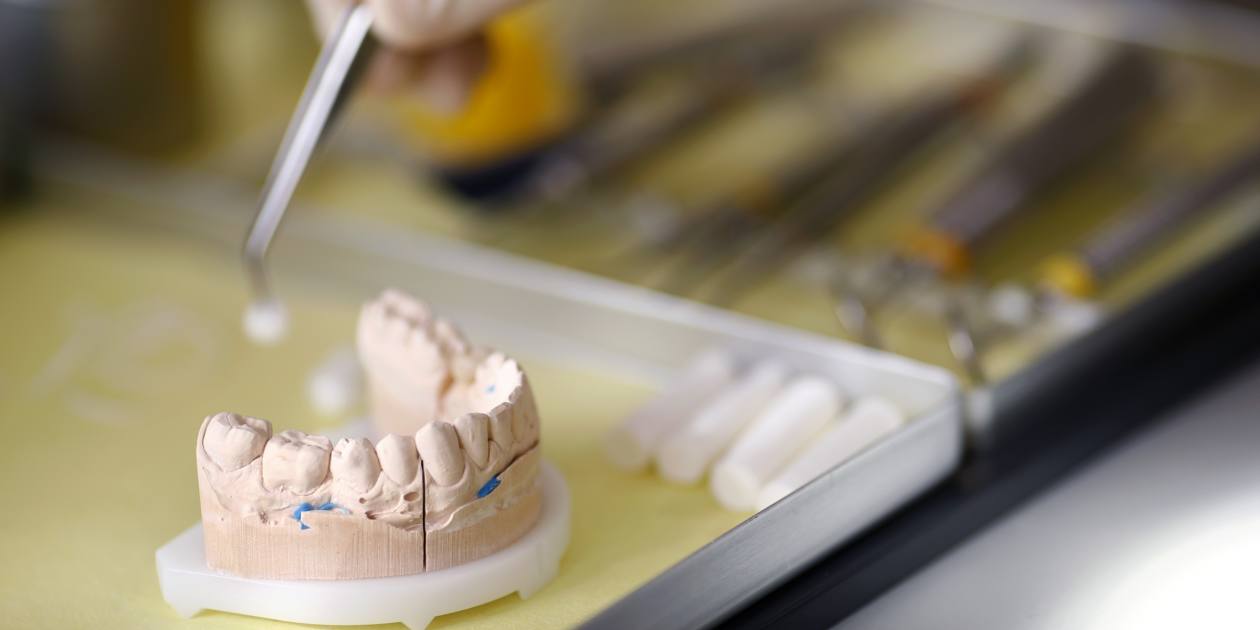
World's first tooth-regenerating drug to enter testing in Japan
Startup aims to roll out antibody treatment in 2030 as alternative to implants
Booker
All-Pro
Offline
West Virginia be like…World's first tooth-regenerating drug to enter testing in Japan
Startup aims to roll out antibody treatment in 2030 as alternative to implantsasia.nikkei.com

Sailorsaint
Guest
- Joined
- Mar 8, 2005
- Messages
- 12,501
- Reaction score
- 21,955
Offline
I was going to say something along the lines of “those that need it the most, won’t be able to afford it”.
- Joined
- Jul 18, 1998
- Messages
- 22,399
- Reaction score
- 46,365
Offline
Not as scary as a cocaine bear but

 www.theguardian.com
www.theguardian.com

‘I see cocaine in wild shrimp in Suffolk’: meet the scientist who analyses our wastewater
Dr Leon Barron studies London’s wastewater, analysing it in all its chemical, narcotic, polluted glory, before and after treatment. Amazingly, he still drinks the stuff from the tap
- Joined
- Jul 18, 1998
- Messages
- 22,399
- Reaction score
- 46,365
Offline
There’s something fishy going on in the water. Across Earth’s oceans, fish are shrinking — and no one can agree why.
It’s happening with salmon near the Arctic Circle and skate in the Atlantic. Nearly three-fourths of marine fish populations sampled worldwide have seen their average body size dwindle between 1960 and 2020, according to a recent analysis.
Overfishing and human-caused climate change are decreasing the size of adult fish, threatening the food supply of more than 3 billion people who rely on seafood as a significant source of protein.
As fish get smaller, there is less meat to cook per catch. So scientists are working to piece together why exactly fish respond to rising ocean temperatures by getting smaller.
“This is a pretty fundamental question,” said Lisa Komoroske, a conservation biologist at the University of Massachusetts at Amherst. “But we still don’t understand why.”
“How is it that we’ve known about this for so long but we don’t understand mechanisms?” she added…….
It’s happening with salmon near the Arctic Circle and skate in the Atlantic. Nearly three-fourths of marine fish populations sampled worldwide have seen their average body size dwindle between 1960 and 2020, according to a recent analysis.
Overfishing and human-caused climate change are decreasing the size of adult fish, threatening the food supply of more than 3 billion people who rely on seafood as a significant source of protein.
As fish get smaller, there is less meat to cook per catch. So scientists are working to piece together why exactly fish respond to rising ocean temperatures by getting smaller.
“This is a pretty fundamental question,” said Lisa Komoroske, a conservation biologist at the University of Massachusetts at Amherst. “But we still don’t understand why.”
“How is it that we’ve known about this for so long but we don’t understand mechanisms?” she added…….
Sailorsaint
Guest
- Joined
- Mar 8, 2005
- Messages
- 12,501
- Reaction score
- 21,955
Offline
I would think warmer water would make them grow larger. Maybe it's the oxygen content instead.There’s something fishy going on in the water. Across Earth’s oceans, fish are shrinking — and no one can agree why.
It’s happening with salmon near the Arctic Circle and skate in the Atlantic. Nearly three-fourths of marine fish populations sampled worldwide have seen their average body size dwindle between 1960 and 2020, according to a recent analysis.
Overfishing and human-caused climate change are decreasing the size of adult fish, threatening the food supply of more than 3 billion people who rely on seafood as a significant source of protein.
As fish get smaller, there is less meat to cook per catch. So scientists are working to piece together why exactly fish respond to rising ocean temperatures by getting smaller.
“This is a pretty fundamental question,” said Lisa Komoroske, a conservation biologist at the University of Massachusetts at Amherst. “But we still don’t understand why.”
“How is it that we’ve known about this for so long but we don’t understand mechanisms?” she added…….

MIT Makes ‘Astonishing’ Discovery That Light Can Vaporize Water Without Heat–for Clean Energy and Desalination
The scientists subjected their findings to 14 different tests and measurements to try and disprove what the they had observed
 www.goodnewsnetwork.org
www.goodnewsnetwork.orgSailorsaint
Guest
- Joined
- Mar 8, 2005
- Messages
- 12,501
- Reaction score
- 21,955
Offline
So, Smart Dust is a thing. And it's scary as hell.....

 builtin.com
builtin.com

What Is Smart Dust? | Built In
Smart dust refers to tiny sensors that suspend in the air and collect data from their surroundings, whether that be combat zones or the inside of a human body.
- Joined
- Jul 18, 1998
- Messages
- 22,399
- Reaction score
- 46,365
Offline
Researchers studying thousands of recorded calls have discovered a kind of “sperm whale phonetic alphabet” embedded in their strings of “click” sounds.
The finding suggests these whales have a communication system considerably more complex than previously thought.
It also adds to almost a century of research on animals and insects that has chipped away at the long-held notion that humans alone possess an intricate system for conversing with one another.
For sperm whales, bursts of clicks known as a codas come in different varieties and form the building blocks of speech, just as human language emerges from the different vocal sounds we combine to form words and sentences.
The whales shape these codas into some 300 types by varying their duration, rhythm and tempo, and sometimes by adding an extra click. The researchers describe their discovery in a study published Tuesday in the journal Nature Communications.
“The very important caveat to add here is that we still don’t know whether you want to think of a coda as being a word, or like a sentence, or like an individual vowel or consonant,” said Jacob Andreas, an associate professor in electrical engineering and computer science at MIT who is one of the authors of the new study…….
The finding suggests these whales have a communication system considerably more complex than previously thought.
It also adds to almost a century of research on animals and insects that has chipped away at the long-held notion that humans alone possess an intricate system for conversing with one another.
For sperm whales, bursts of clicks known as a codas come in different varieties and form the building blocks of speech, just as human language emerges from the different vocal sounds we combine to form words and sentences.
The whales shape these codas into some 300 types by varying their duration, rhythm and tempo, and sometimes by adding an extra click. The researchers describe their discovery in a study published Tuesday in the journal Nature Communications.
“The very important caveat to add here is that we still don’t know whether you want to think of a coda as being a word, or like a sentence, or like an individual vowel or consonant,” said Jacob Andreas, an associate professor in electrical engineering and computer science at MIT who is one of the authors of the new study…….
- Moderator
- #2,847
Offline
Would have never guessed that was developed at BerkleySo, Smart Dust is a thing. And it's scary as hell.....
What Is Smart Dust? | Built In
Smart dust refers to tiny sensors that suspend in the air and collect data from their surroundings, whether that be combat zones or the inside of a human body.builtin.com
- Joined
- Jul 18, 1998
- Messages
- 22,399
- Reaction score
- 46,365
Offline
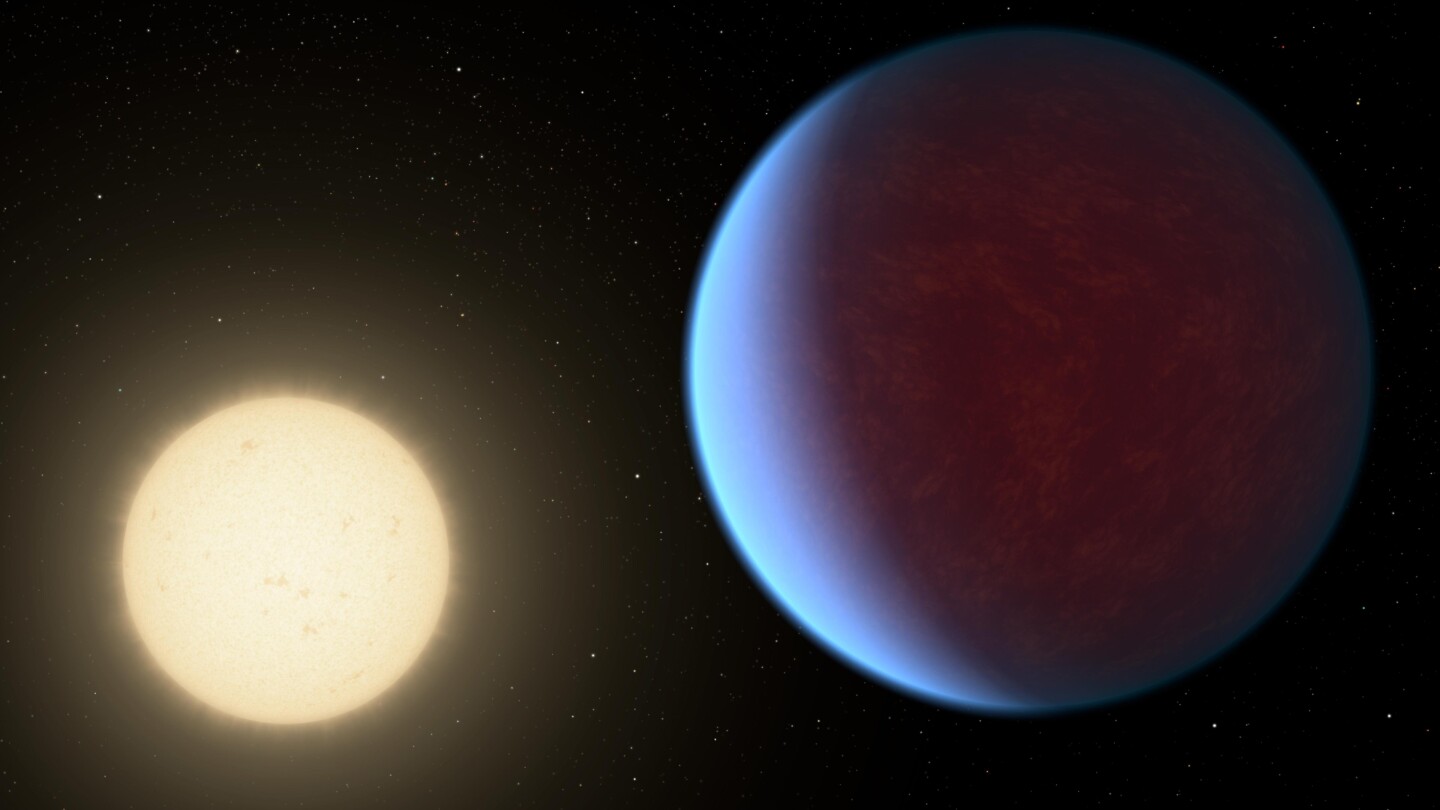
DALLAS (AP) — A thick atmosphere has been detected around a planet that’s twice as big as Earth in a nearby solar system, researchers reported Wednesday.
The so-called super Earth — known as 55 Cancri e — is among the few rocky planets outside our solar system with a significant atmosphere, wrapped a blanket of carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. The exact amounts are unclear. Earth’s atmosphere is a blend of nitrogen, oxygen, argon and other gases.
“It’s probably the firmest evidence yet that this planet has an atmosphere,” said Ian Crossfield, an astronomer at the University of Kansas who studies exoplanets and was not involved with the research.
The research was published in the journal Nature.
Super Earth refers to a planet’s size — bigger than Earth but smaller than Neptune. The boiling temperatures on this planet — which can reach as hot as 4,200 degrees Fahrenheit (2,300 degrees Celsius) – mean that it is unlikely to host life.
Instead, scientists say the discovery is a promising sign that other such rocky planets with thick atmospheres could exist that may be more hospitable.
The exoplanet 41 light years away is eight times heavier than Earth and circles its star Copernicus so closely that it has permanent day and night sides. A light-year is nearly 6 trillion miles (9.7 trillion kilometers). Its surface is encrusted with magma oceans.……

 apnews.com
apnews.com
The so-called super Earth — known as 55 Cancri e — is among the few rocky planets outside our solar system with a significant atmosphere, wrapped a blanket of carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. The exact amounts are unclear. Earth’s atmosphere is a blend of nitrogen, oxygen, argon and other gases.
“It’s probably the firmest evidence yet that this planet has an atmosphere,” said Ian Crossfield, an astronomer at the University of Kansas who studies exoplanets and was not involved with the research.
The research was published in the journal Nature.
Super Earth refers to a planet’s size — bigger than Earth but smaller than Neptune. The boiling temperatures on this planet — which can reach as hot as 4,200 degrees Fahrenheit (2,300 degrees Celsius) – mean that it is unlikely to host life.
Instead, scientists say the discovery is a promising sign that other such rocky planets with thick atmospheres could exist that may be more hospitable.
The exoplanet 41 light years away is eight times heavier than Earth and circles its star Copernicus so closely that it has permanent day and night sides. A light-year is nearly 6 trillion miles (9.7 trillion kilometers). Its surface is encrusted with magma oceans.……
A scorching, rocky planet twice Earth's size has a thick atmosphere, scientists say
A thick atmosphere has been detected around a planet that's twice as big as Earth in a nearby solar system.
Sailorsaint
Guest
- Joined
- Mar 8, 2005
- Messages
- 12,501
- Reaction score
- 21,955
Offline
Just because the atmosphere is poisonous to us and the temperature is too high, doesn't mean there isn't life there.DALLAS (AP) — A thick atmosphere has been detected around a planet that’s twice as big as Earth in a nearby solar system, researchers reported Wednesday.
The so-called super Earth — known as 55 Cancri e — is among the few rocky planets outside our solar system with a significant atmosphere, wrapped a blanket of carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. The exact amounts are unclear. Earth’s atmosphere is a blend of nitrogen, oxygen, argon and other gases.
“It’s probably the firmest evidence yet that this planet has an atmosphere,” said Ian Crossfield, an astronomer at the University of Kansas who studies exoplanets and was not involved with the research.
The research was published in the journal Nature.
Super Earth refers to a planet’s size — bigger than Earth but smaller than Neptune. The boiling temperatures on this planet — which can reach as hot as 4,200 degrees Fahrenheit (2,300 degrees Celsius) – mean that it is unlikely to host life.
Instead, scientists say the discovery is a promising sign that other such rocky planets with thick atmospheres could exist that may be more hospitable.
The exoplanet 41 light years away is eight times heavier than Earth and circles its star Copernicus so closely that it has permanent day and night sides. A light-year is nearly 6 trillion miles (9.7 trillion kilometers). Its surface is encrusted with magma oceans.……
A scorching, rocky planet twice Earth's size has a thick atmosphere, scientists say
A thick atmosphere has been detected around a planet that's twice as big as Earth in a nearby solar system.apnews.com

- Joined
- Jul 18, 1998
- Messages
- 22,399
- Reaction score
- 46,365
Offline
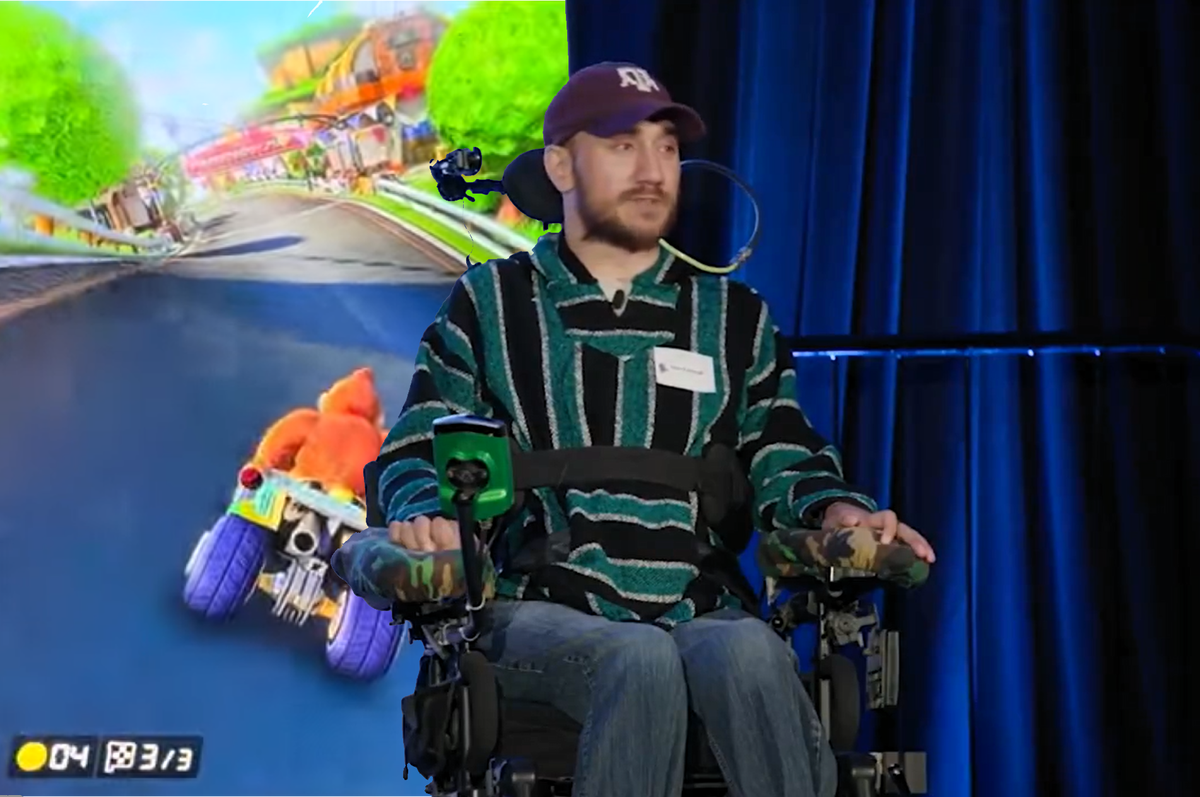
Participants in the first human trials of the Neuralink brain chip have revealed that they have been using the technology to play video games for up to 12 hours per day.
Neuralink shared details from the first 100 days of its PRIME Study, which saw paralysed people surgically fitted with a brain-machine interface in order to give them control of a computer using just their thoughts……

 www.independent.co.uk
www.independent.co.uk
Neuralink shared details from the first 100 days of its PRIME Study, which saw paralysed people surgically fitted with a brain-machine interface in order to give them control of a computer using just their thoughts……

First human with Neuralink brain chip uses it to play Mario Kart telepathically
‘I’m beating my friends in games that as a quadriplegic I should not be beating them in,’ says Neuralink wearer